What is Thermochemical Processing?
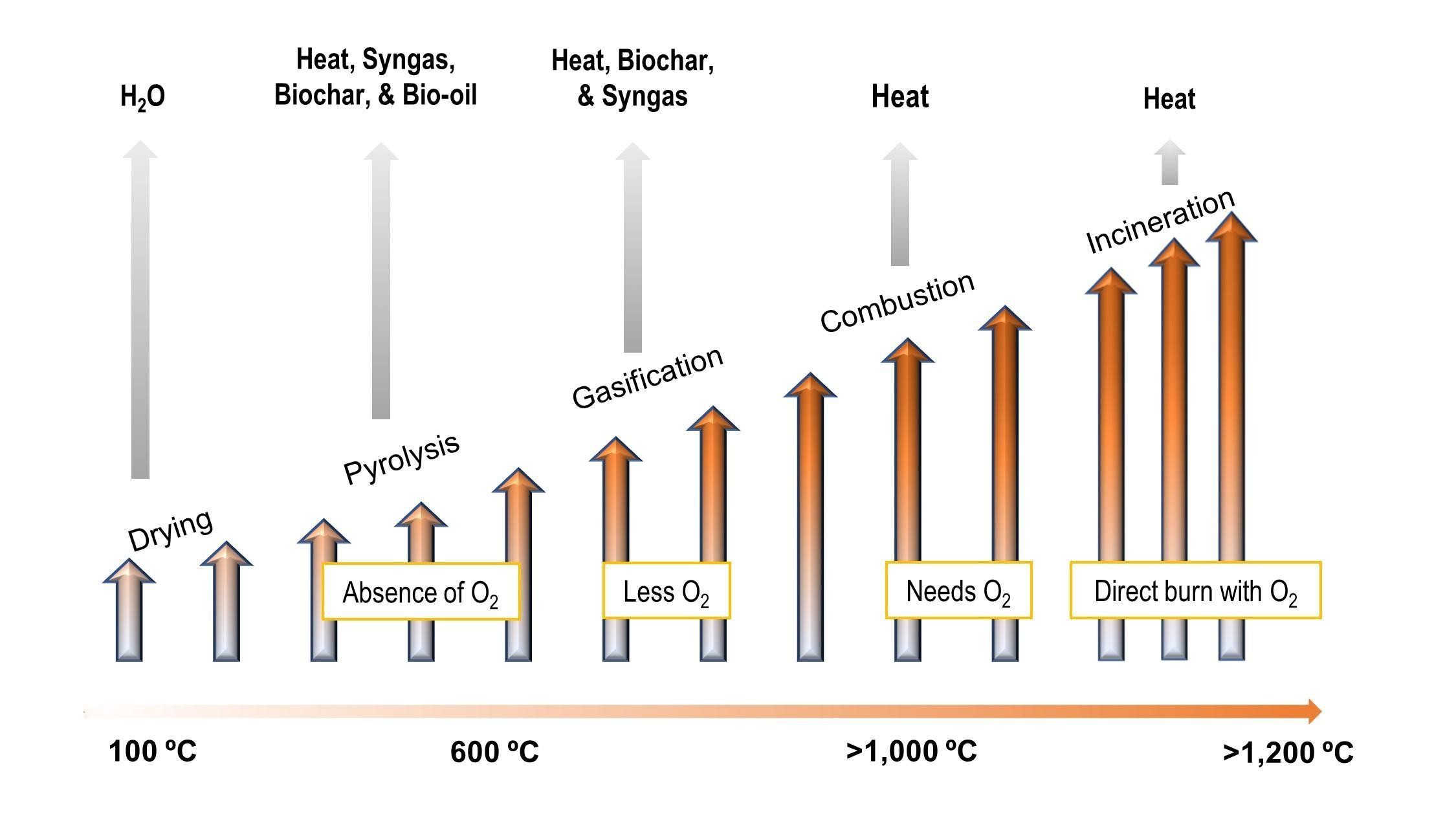
Thermochemical processing is a high-heat way to turn farm waste into fuel, fertilizer, and other useful products. Farm waste like poultry litter can be processed at high temperatures into things like bio-oil, biochar, or gas, using heat and special systems.
How it Works
- If waste is heated, when there's no oxygen → it produces biochar and bio-oil (this is called pyrolysis)
- If waste is heated, when there's some oxygen → it makes heat and gas (this is gasification)
- If waste is heated, when there's a lot of oxygen → it just burns (incineration or combustion)
Why it Matters for Farmers & Landowners
- Turns hard to manage waste into something valuable
- Reduce harmful gas emissions
- Can power equipment, heat barns, or improve soil (if using biochar)
- Useful for poultry farms, large-scale livestock, or food waste systems
Recommended for First-Time Visitors
Thermochemical Processing Fact Sheet - A Quick Summary
Language Versions
Itilize Pwosesis Tèmochimik pou Jere fatra/ dechè Agrikòl (Kreyòl ayisyen)Uso de Procesos Termoquímicos Para el Manejo de Residuos Agrícolas (Español)