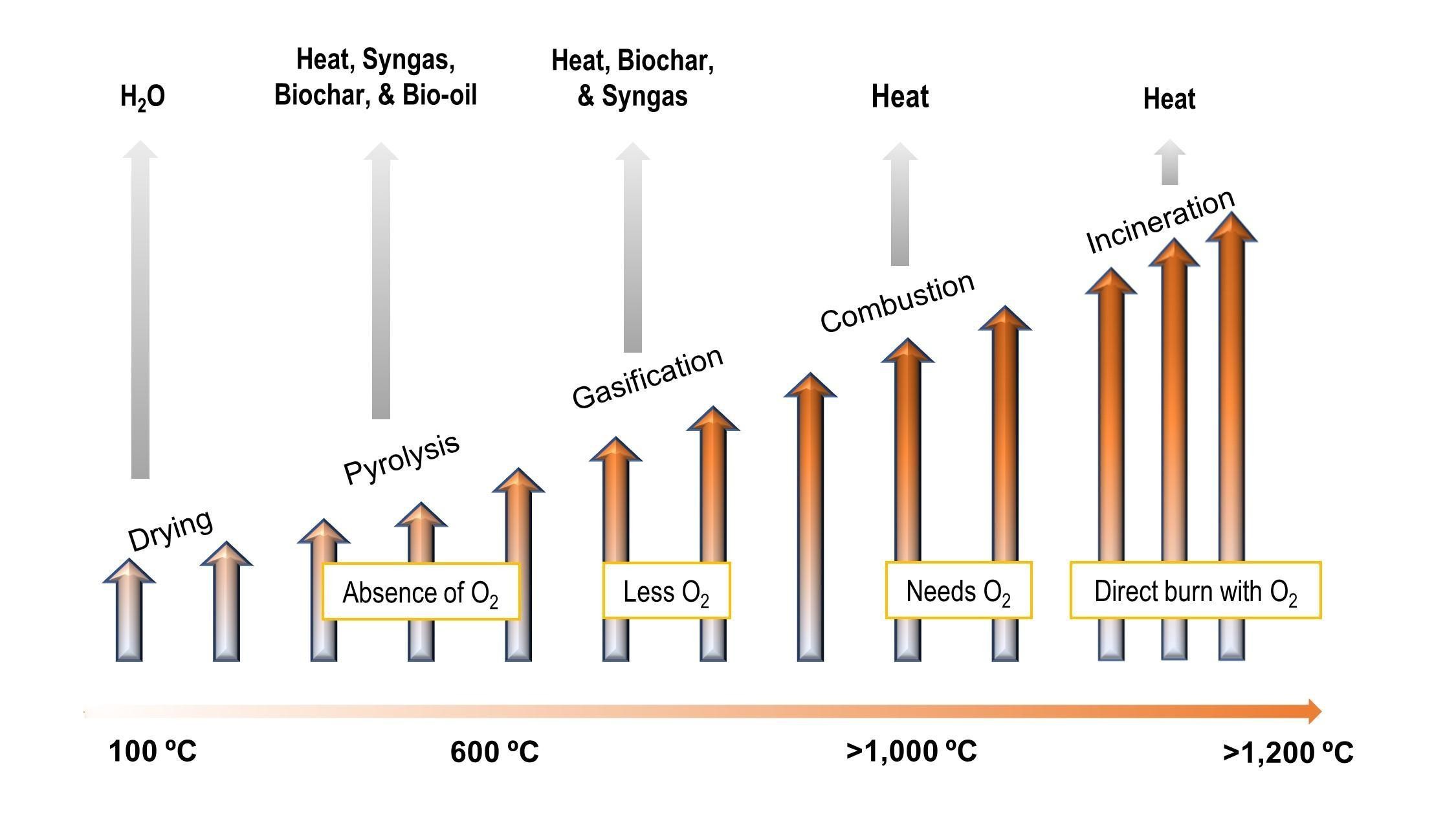
As poultry litter operations grow in the Delmarva region, farmers, haulers, and managers face a challenge in handling this low-moisture biomass in an eco-friendly manner. Thermochemical processing is a waste to energy alternative to field application, where solid, low-moisture organic materials are processed into value-added products, including renewable energy. Thermochemical processing includes gasification, pyrolysis, combustion, and incineration. Each process not only reduces the total volume of biomass but also can reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with anaerobic decomposition and can create beneficial value-added products.
Depending on the specific thermochemical processing utilized, the following byproducts could be formed:
- Biochar: A stable carbon product enhancing soil health, water retention, which acts as a carbon sink.
- Bio-oil: A viscous liquid with potential applications in biofuel production, chemical processes, and heating.
- Syngas: A gas mixture mainly of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, serving as a versatile renewable energy source.
Thermochemical Processing Fact Sheet
Itilize Pwosesis Tèmochimik pou Jere fatra/ dechè Agrikòl (Kreyòl ayisyen)
Uso de Procesos Termoquímicos Para el Manejo de Residuos Agrícolas (Español)